Unveiling the intricacies of matter, the chemistry atomic structure worksheet with answers embarks on a captivating journey into the fundamental building blocks of our universe. By exploring the arrangement and properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons within atoms, this comprehensive guide unravels the secrets that govern chemical reactions and shape the world around us.
Delving into the depths of electron configuration, periodic trends, and chemical bonding, this worksheet empowers learners with a profound understanding of atomic structure and its profound implications. With a wealth of engaging examples and insightful explanations, it serves as an invaluable resource for students, educators, and anyone seeking to unravel the mysteries of the atomic realm.
Atomic Structure Overview
An atom is the fundamental building block of matter. It consists of a dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while the electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels called shells.
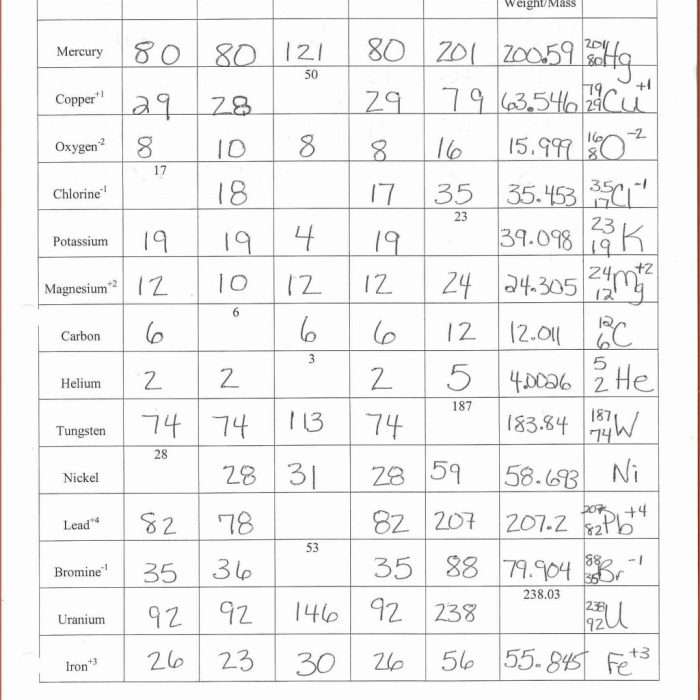
The number of protons in the nucleus defines the element’s atomic number and its position on the periodic table. The number of neutrons determines the isotope of the element.
Electron Configuration
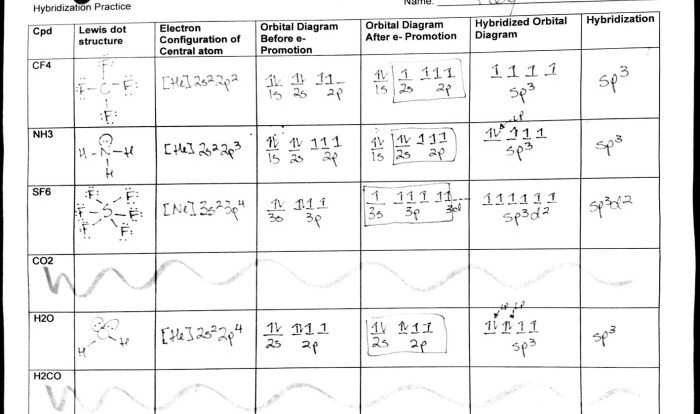
Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in the energy levels or shells around the nucleus. The first energy level can hold a maximum of two electrons, the second energy level can hold a maximum of eight electrons, and so on.
The electron configuration of an element determines its chemical properties. For example, elements with a full outer energy level are stable and less likely to react with other elements.
Periodic Trends
The periodic table is organized based on the atomic number of the elements. Elements with similar electron configurations are grouped together, and these groups exhibit periodic trends in their properties.
For example, as you move across a period (row) from left to right, the elements become more electronegative and have a higher ionization energy. As you move down a group (column), the elements become more metallic and have a lower ionization energy.
Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding is the process by which atoms combine to form molecules or compounds. There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic.
Ionic bonds are formed between atoms that have opposite charges. Covalent bonds are formed between atoms that share electrons. Metallic bonds are formed between atoms in a metal lattice.
Applications of Atomic Structure, Chemistry atomic structure worksheet with answers
The understanding of atomic structure has led to numerous technological advancements. For example, the development of the transistor, the basis of modern computers, was made possible by the understanding of semiconductor materials.
Atomic structure is also used in fields such as chemistry, materials science, and medicine. For example, the understanding of electron configurations can be used to predict the reactivity of elements and design new materials.
General Inquiries: Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet With Answers
What is atomic structure?
Atomic structure refers to the arrangement and properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom, which determine its chemical behavior.
How does electron configuration influence atomic properties?
Electron configuration, which describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom, significantly affects its chemical reactivity, bonding behavior, and other properties.
What are the key periodic trends observed in atomic structure?
Periodic trends include the variation in atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and other properties across the periodic table, which can be explained by changes in atomic structure.
How does atomic structure influence chemical bonding?
Atomic structure determines the number and arrangement of valence electrons, which play a crucial role in forming chemical bonds between atoms.
What are some practical applications of understanding atomic structure?
Understanding atomic structure has applications in fields such as chemistry, materials science, medicine, and nanotechnology, enabling the development of new materials, drugs, and technologies.