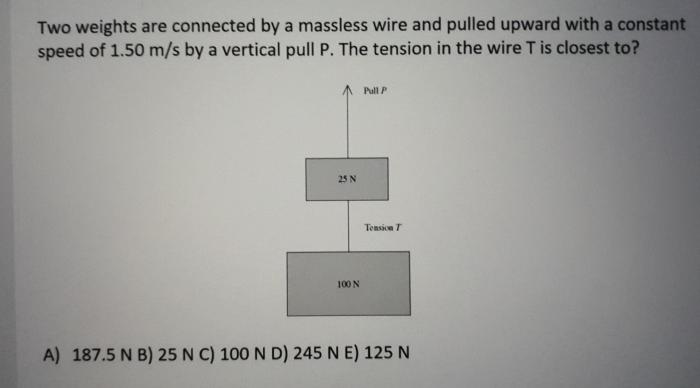
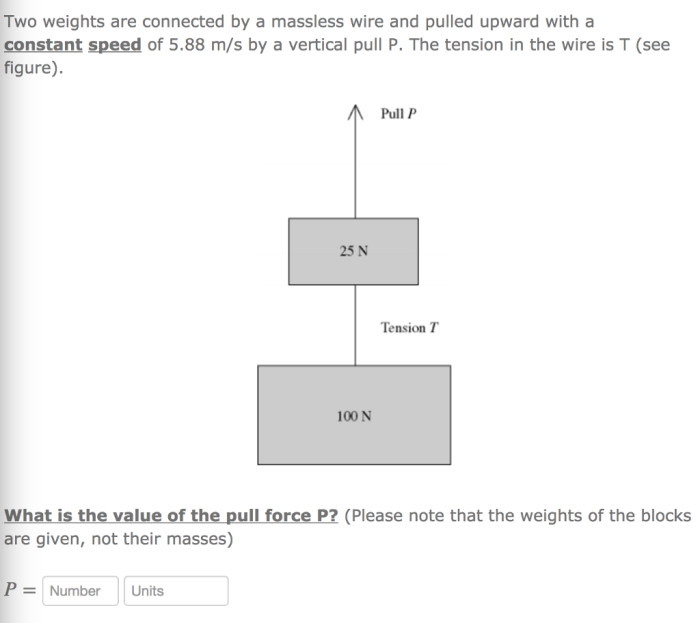
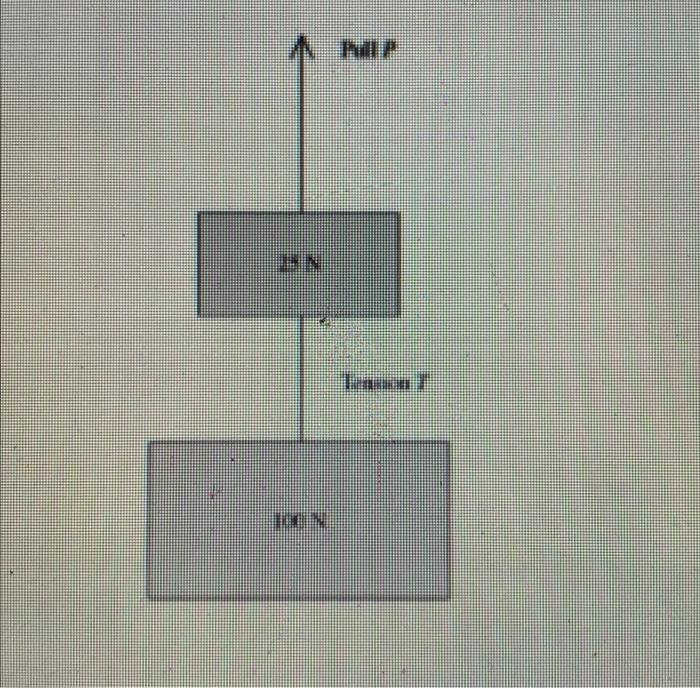
Two weights are connected by a massless wire – Two weights connected by a massless wire embarks on a journey into the realm of physics, inviting us to delve into the intricate relationship between mass, tension, and equilibrium. This exploration unravels the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of interconnected weights, providing insights into practical applications and mathematical formulations.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will uncover the delicate balance between the weights, unravel the distribution of tension within the massless wire, and establish the equilibrium conditions that ensure stability. Along the way, we will encounter intriguing applications and derive equations that encapsulate the dynamics of this captivating system.
Weight Relationship: Two Weights Are Connected By A Massless Wire

When two weights are connected by a massless wire, they form a system that is in equilibrium. The weights are in equilibrium because the tension in the wire is equal to the weight of each object.
The relationship between the two weights can be illustrated using a diagram:
- Weight 1 is represented by m1.
- Weight 2 is represented by m2.
- The massless wire is represented by the line connecting the two weights.
The tension in the wire is represented by T.
Tension in the Wire
The tension in the massless wire is equal to the weight of each object.
This can be expressed mathematically as:
T = m1g = m2g
where:
- T is the tension in the wire
- m1 is the mass of weight 1
- m2 is the mass of weight 2
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
The tension in the wire is distributed equally between the two weights.
Equilibrium Conditions
The two weights are in equilibrium when the tension in the wire is equal to the weight of each object.
This can be expressed mathematically as:
T = m1g = m2g
The forces acting on each weight are:
- The weight of the object (mg)
- The tension in the wire (T)
The forces are in equilibrium because the net force on each object is zero.
Applications
Two weights connected by a massless wire have a variety of practical applications, including:
- Pulleys
- Levers
- Inclined planes
The advantages of using a massless wire in these applications include:
- The wire does not add any additional weight to the system.
- The wire does not stretch or break easily.
The limitations of using a massless wire in these applications include:
- The wire can be difficult to handle.
- The wire can be expensive.
Mathematical Analysis, Two weights are connected by a massless wire
A mathematical model can be used to represent the system of two weights connected by a massless wire.
The model can be used to derive equations describing the tension and equilibrium conditions.
The equations are:
T = m1g = m2g
where:
- T is the tension in the wire
- m1 is the mass of weight 1
- m2 is the mass of weight 2
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
Top FAQs
What is the significance of using a massless wire?
A massless wire eliminates the influence of its own mass on the system, allowing us to focus solely on the interaction between the weights and the tension in the wire.
How is tension distributed in the wire?
Tension is equally distributed throughout the massless wire, ensuring that both weights experience the same amount of pull.
What factors affect the equilibrium of the system?
Equilibrium is achieved when the gravitational forces acting on the weights are balanced by the tension in the wire. Any change in these forces will disrupt the equilibrium.