Embark on a journey into the realm of biology as we delve into the captivating world of types of tissue concept map. This guide will unravel the intricate tapestry of life, exploring the diverse array of tissues that orchestrate the symphony of our bodies.
From the protective layers of epithelial tissue to the dynamic contractile nature of muscle tissue, each type plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis, providing support, facilitating movement, and enabling communication within the body.
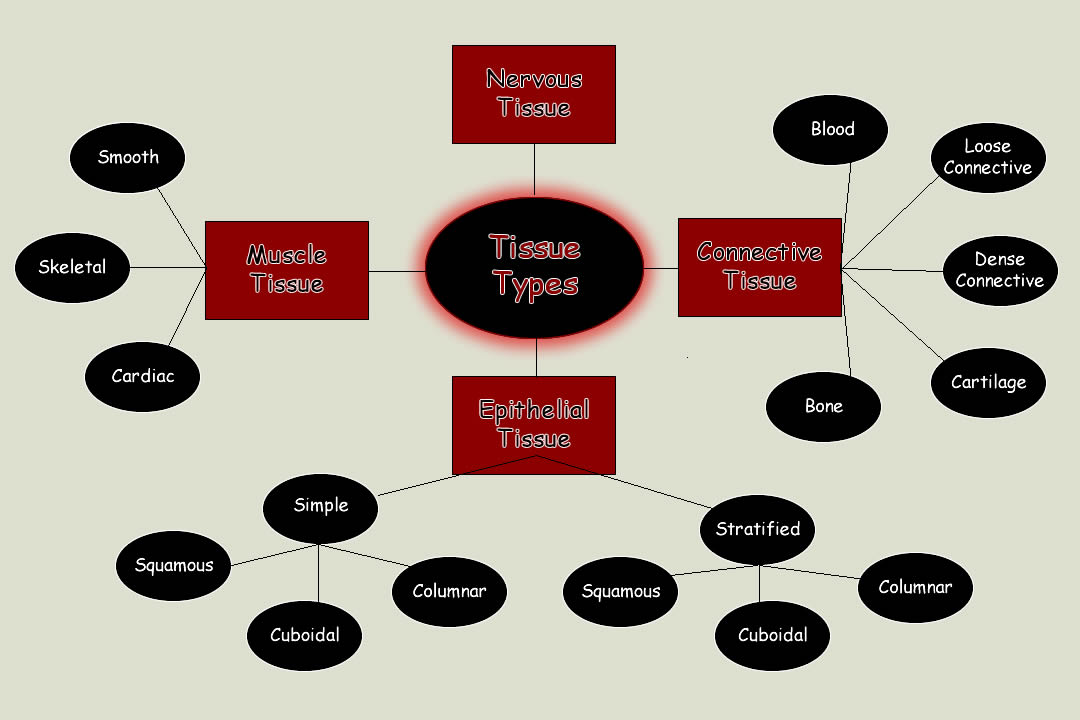
Types of Tissue Overview
Tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Tissues are the building blocks of organs, which are groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function.
There are four levels of tissue organization:
- Cells:The basic unit of life, cells are the smallest living things that can carry out all the functions of life.
- Tissues:Groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
- Organs:Groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function.
- Organ systems:Groups of organs that work together to perform a specific function.
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that covers the surfaces of the body, lines the internal organs, and forms glands. It is composed of closely packed cells that form a protective barrier between the body and its environment. Epithelial tissue has a variety of functions, including:
- Protection: Epithelial tissue protects the body from physical, chemical, and biological damage.
- Secretion: Epithelial tissue secretes substances such as hormones, enzymes, and mucus.
- Absorption: Epithelial tissue absorbs nutrients and other substances from the environment.
- Excretion: Epithelial tissue excretes waste products from the body.
There are different types of epithelial tissue, each with its own unique structure and function. Some of the most common types of epithelial tissue include:
- Simple squamous epithelium: This type of epithelium is composed of a single layer of flat cells. It is found in areas where diffusion or filtration occurs, such as the lining of blood vessels and alveoli in the lungs.
- Simple cuboidal epithelium: This type of epithelium is composed of a single layer of cube-shaped cells. It is found in areas where secretion or absorption occurs, such as the lining of the kidney tubules and salivary glands.
- Simple columnar epithelium: This type of epithelium is composed of a single layer of tall, column-shaped cells. It is found in areas where absorption or secretion occurs, such as the lining of the small intestine and stomach.
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium: This type of epithelium appears to be composed of multiple layers of cells, but in reality, it is composed of a single layer of cells that are different heights. It is found in areas where cilia are present, such as the lining of the trachea and bronchi.
- Stratified squamous epithelium: This type of epithelium is composed of multiple layers of cells. The cells in the deepest layer are cuboidal or columnar, while the cells in the superficial layer are flat. It is found in areas where there is a lot of wear and tear, such as the skin and the lining of the esophagus.
Epithelial tissue plays an important role in homeostasis. It helps to maintain the body’s internal environment by regulating the passage of substances into and out of the body. It also helps to protect the body from infection and injury.
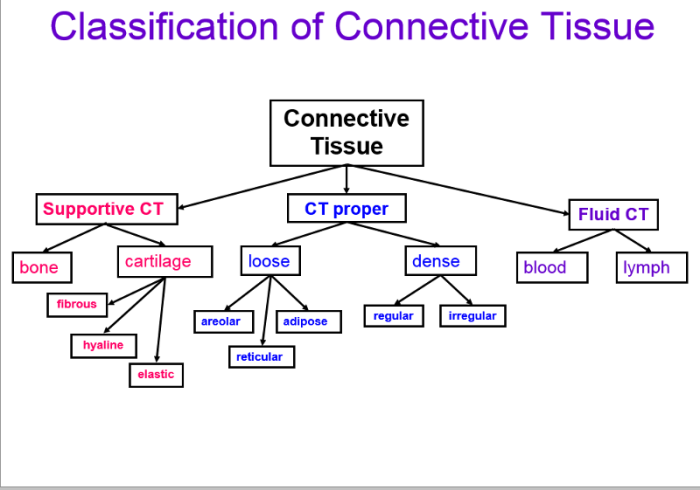
Connective Tissue
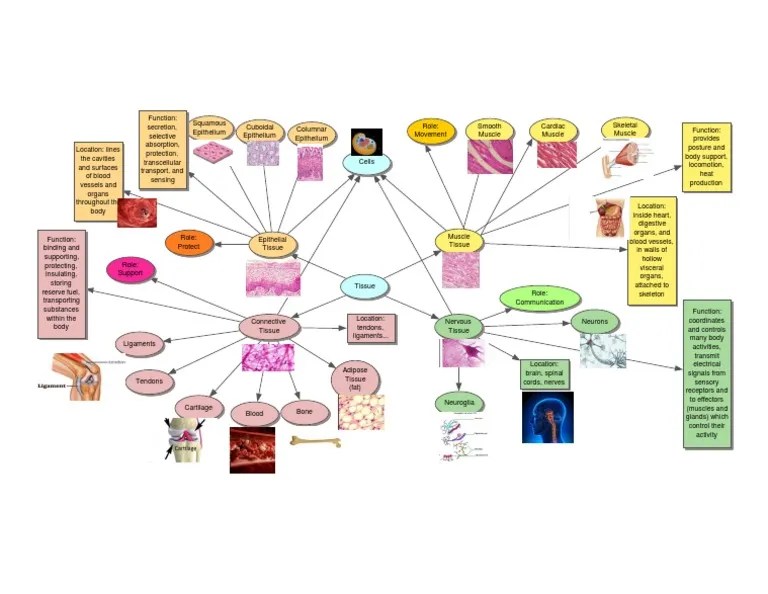
Connective tissue, the most abundant tissue type in the body, is characterized by its specialized cells and extracellular matrix. It provides support, protection, and connects various organs and tissues in the body.
Connective tissue consists of three main components: cells, fibers, and ground substance. The cells secrete the extracellular matrix, which is composed of fibers and ground substance. The fibers provide strength and flexibility, while the ground substance fills the spaces between cells and fibers, providing support and cushioning.
Types of Connective Tissue
- Loose Connective Tissue:Contains loosely arranged cells and fibers in a gelatinous ground substance. It is found in the subcutaneous layer, around blood vessels, and in organs.
- Dense Connective Tissue:Has tightly packed fibers and fewer cells. It provides strength and support to structures like tendons, ligaments, and bones.
- Cartilage:A specialized connective tissue that provides support and flexibility. It is found in joints, ears, and the respiratory tract.
- Bone:A mineralized connective tissue that provides support and protection. It forms the skeleton and protects internal organs.
- Blood:A fluid connective tissue that transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body.
Role of Connective Tissue in Support and Protection, Types of tissue concept map
Connective tissue plays a crucial role in providing support and protection to various structures in the body:
- Skeletal Support:Bones and cartilage provide structural support to the body, enabling movement and protection of internal organs.
- Protection:Dense connective tissue, such as tendons and ligaments, protects and stabilizes joints, muscles, and organs.
- Wound Healing:Connective tissue plays a vital role in wound healing by forming a protective barrier and providing a framework for tissue regeneration.
Muscle Tissue: Types Of Tissue Concept Map
Muscle tissue, a specialized tissue in animals, is responsible for movement, posture, and heat production. It comprises elongated cells called muscle fibers that contain contractile proteins. These proteins enable muscle tissue to shorten and lengthen, generating the force necessary for movement.Muscle
tissue plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including locomotion, respiration, digestion, and circulation. It provides structural support, maintains body temperature, and facilitates the movement of substances within the body.
Types of Muscle Tissue
There are three main types of muscle tissue:
Skeletal muscle
Attached to bones, skeletal muscle enables voluntary movement. It is striated, meaning it has alternating light and dark bands visible under a microscope.
Cardiac muscle
Found exclusively in the heart, cardiac muscle is responsible for the rhythmic contractions that pump blood throughout the body. It is striated and involuntary, meaning it contracts without conscious control.
Smooth muscle
Found in the walls of hollow organs like the stomach and blood vessels, smooth muscle controls involuntary functions such as digestion and blood flow regulation. It is non-striated and contracts slowly and rhythmically.
If you’re trying to wrap your head around the types of tissue concept map, then check out the proctored ati med surg 2019 . It’s a great resource that can help you understand the basics of this complex topic. Then, you can come back here and dive deeper into the different types of tissue and their functions.
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is a specialized type of tissue that forms the nervous system, which is responsible for communication and control within the body. It is composed of two main types of cells: neurons and neuroglia.
Neurons
Neurons are the functional units of the nervous system. They are specialized cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. Neurons have three main parts:
- Cell body:The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles responsible for the cell’s metabolism.
- Dendrites:Dendrites are short, branched extensions of the cell body that receive signals from other neurons.
- Axon:The axon is a long, thin extension of the cell body that transmits signals to other neurons or muscles.
Neuroglia
Neuroglia are cells that support and protect neurons. They make up about 90% of the cells in the nervous system. There are several types of neuroglia, including:
- Astrocytes:Astrocytes are star-shaped cells that provide structural support and regulate the chemical environment around neurons.
- Oligodendrocytes:Oligodendrocytes are cells that wrap around axons and form a myelin sheath, which insulates the axon and speeds up the transmission of signals.
- Microglia:Microglia are phagocytic cells that remove damaged neurons and debris from the nervous system.
Role of Nervous Tissue in Communication and Control
Nervous tissue plays a crucial role in communication and control within the body. Neurons transmit signals from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord, where the signals are processed and responses are generated. These responses are then transmitted back to muscles and glands, which carry out the appropriate actions.
The nervous system is responsible for a wide range of functions, including:
- Sensory perception
- Motor control
- Cognition
- Emotion
- Memory
Top FAQs
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue forms protective barriers, lining the surfaces of organs and cavities, and regulates the passage of substances.
How does connective tissue provide support and protection?
Connective tissue contains specialized cells and fibers that provide structural support, cushion organs, and protect against mechanical stress.
What is the role of muscle tissue in the body?
Muscle tissue generates force and movement, enabling locomotion, posture, and organ function.
How does nervous tissue facilitate communication?
Nervous tissue transmits electrical and chemical signals, allowing for rapid communication and coordination between different parts of the body.
